
The hair cells are responsible for converting the mechanical energy of the fluid wave into an electrical signal, which will be processed by the brain.
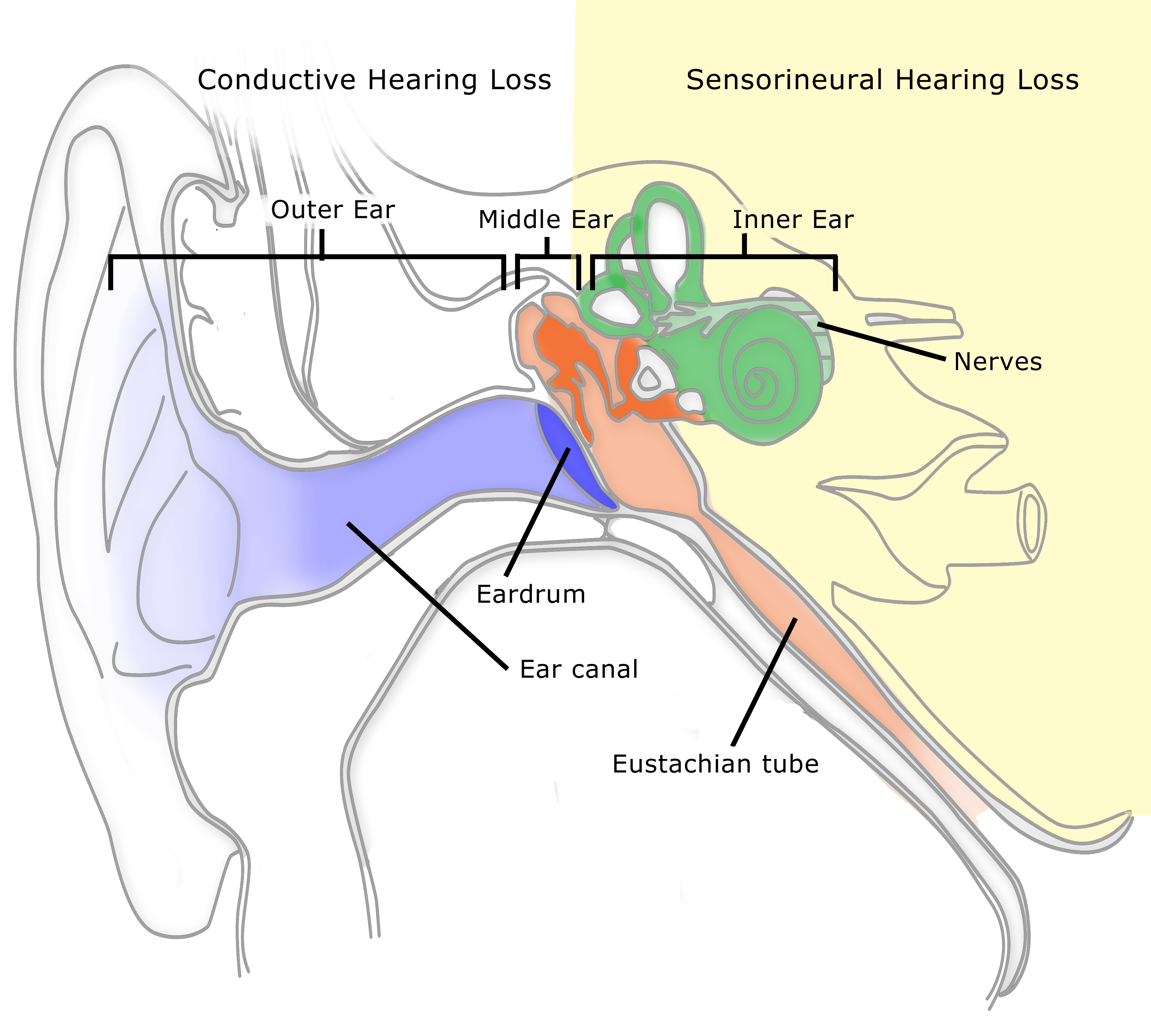
This “traveling wave” in turn activates the hair cells of the organ of Corti, causing the hearing nerve to be activated. The piston-like action of the stapes bone (stirrup) initiates a fluid wave within the perilymph of the scala vestibule. This subsequently produces movement of the middle ear bones. Hearing occurs as sound enters the outer ear canal and causes vibrations of the tympanic membrane (eardrum).

The three semi-circular canals and two otolithic organs orientate our body in three dimensional space. The inner ear is also responsible for sensation of motion and helps with balance. This type of impairment is not correctable with surgery. Most often, this type of hearing impairment is due to a hair cell loss. A disturbance in the inner ear fluids, hair cells, nerve endings, or hearing nerve may result in a sensorineural hearing impairment. Inner ear fluid waves move the delicate hair cells, which in turn excite the hearing nerve endings and transmit sound energy information by the hearing nerve to the brain, where it is interpreted into sound. The inner ear contains microscopic hair cells connected to hearing nerve endings. This type of impairment is usually correctable medically or surgically. A disturbance of the eustachian tube, eardrum, or the ear bones may result in a conductive hearing impairment, meaning impairment of sound conduction to the inner ear. In so doing they act as a transformer, converting sound vibrations in the external ear canal into fluid waves in the inner ear. These structures transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear. The middle ear consists of an eardrum and three small ear bones (ossicles): the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). This chamber is normally air filled and connected to the back of the throat (pharynx) by the eustachian tube, which serves as a pressure-equalizing valve. The middle ear chamber lies between the external and inner ear behind the eardrum.

These structures gather the sound and direct it towards the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The outer ear consists of the auricle and the ear canal. Each part performs an important function in the process of hearing and balance. The ear is comprised of three portions: an outer ear (external), a middle ear, and an inner ear. Meniere’s Disease – Vertigo Balance Disorder.Risks and Potential Complications of Surgery.Surgical Treatment of Dizziness & Meniere’s Disease.Surgical Treatment of Ear Infection, Eardrum Perforation & Cholesteatoma.Meniere’s Disease/Endolymphatic Hydrops.The inner ear also contains the vestibular organ that is responsible for balance. The brain then interprets these signals as sound and this is how we hear.

These nerve endings transform the vibrations into electrical impulses that travel along the auditory nerve to the brain. As the fluid moves, thousands of nerve endings are then set into motion. The cochlea is filled with a fluid that moves in response to the vibrations from the oval window. Once the sound waves enter the inner ear, they travel into a snail shaped organ called the cochlea. The Eustachian tube, which opens into the middle ear, is responsible for equalizing the pressure between the air outside the ear to that within the middle ear. The stapes attaches to the oval window that connects the middle ear to the inner ear. These bones work in conjunction to further amplify the sound. The ossicles are three tiny bones, the smallest in the human body, and are named the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The vibrations from the eardrum then set the ossicles into motion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
